In today’s rapidly evolving IT landscape, automation is key to efficient and scalable infrastructure management. Spring Boot, a popular Java-based framework for building web applications, combined with Ansible, a robust automation tool, offers a potent solution for orchestrating server setup and configuration. This guide will walk you through the process of using Ansible to automate the deployment of a Spring Boot application, streamlining the setup, configuration, and management of your server infrastructure.
Prerequisites
These are the following things that you should need before starting the setup.
- One EC2 instance (amazonlinux 2) as Ansible master server.
- One EC2 instance (amazonlinux 2) as a remote server.
Install pip and ansible in the Amazonlinux 2 server.
- SSH to your Amazon Linux server
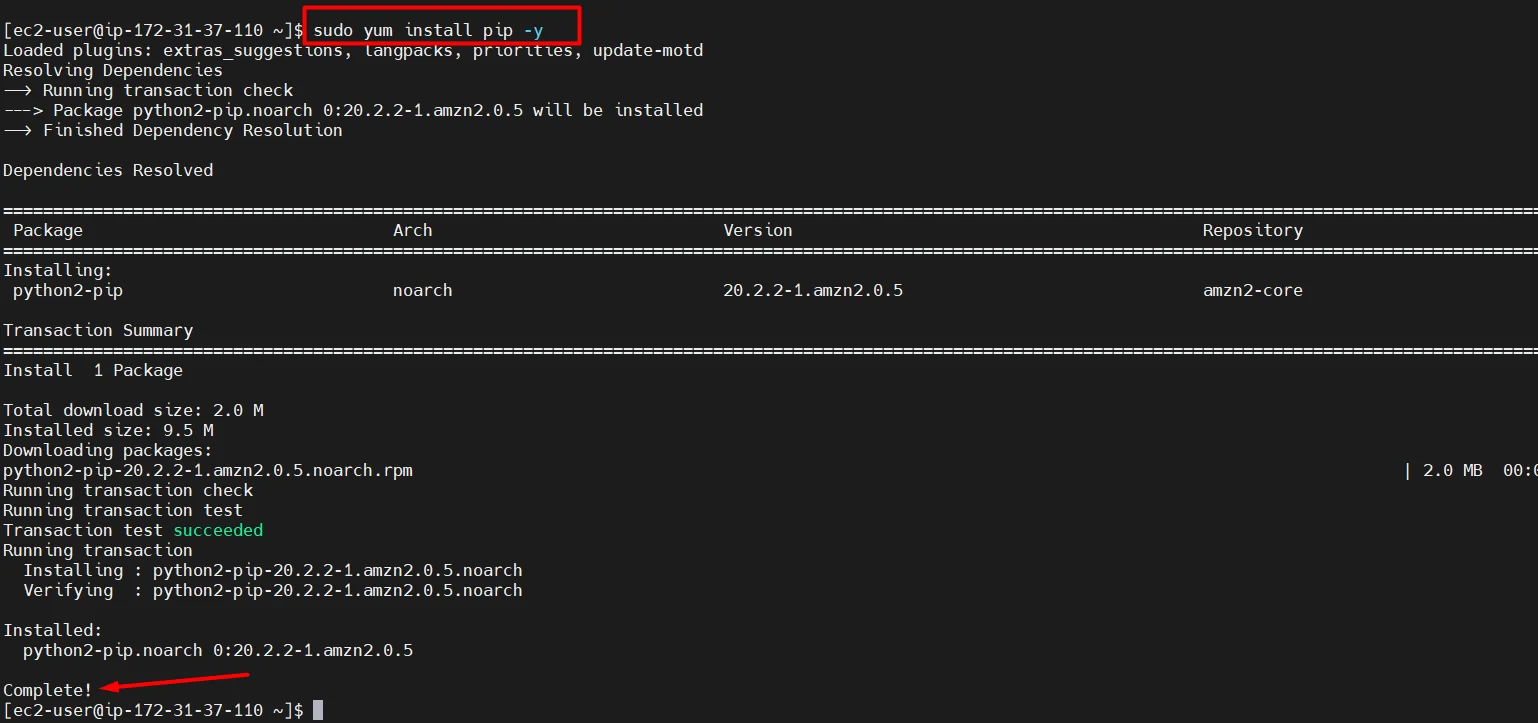
- Install pip
sudo yum install pip -y
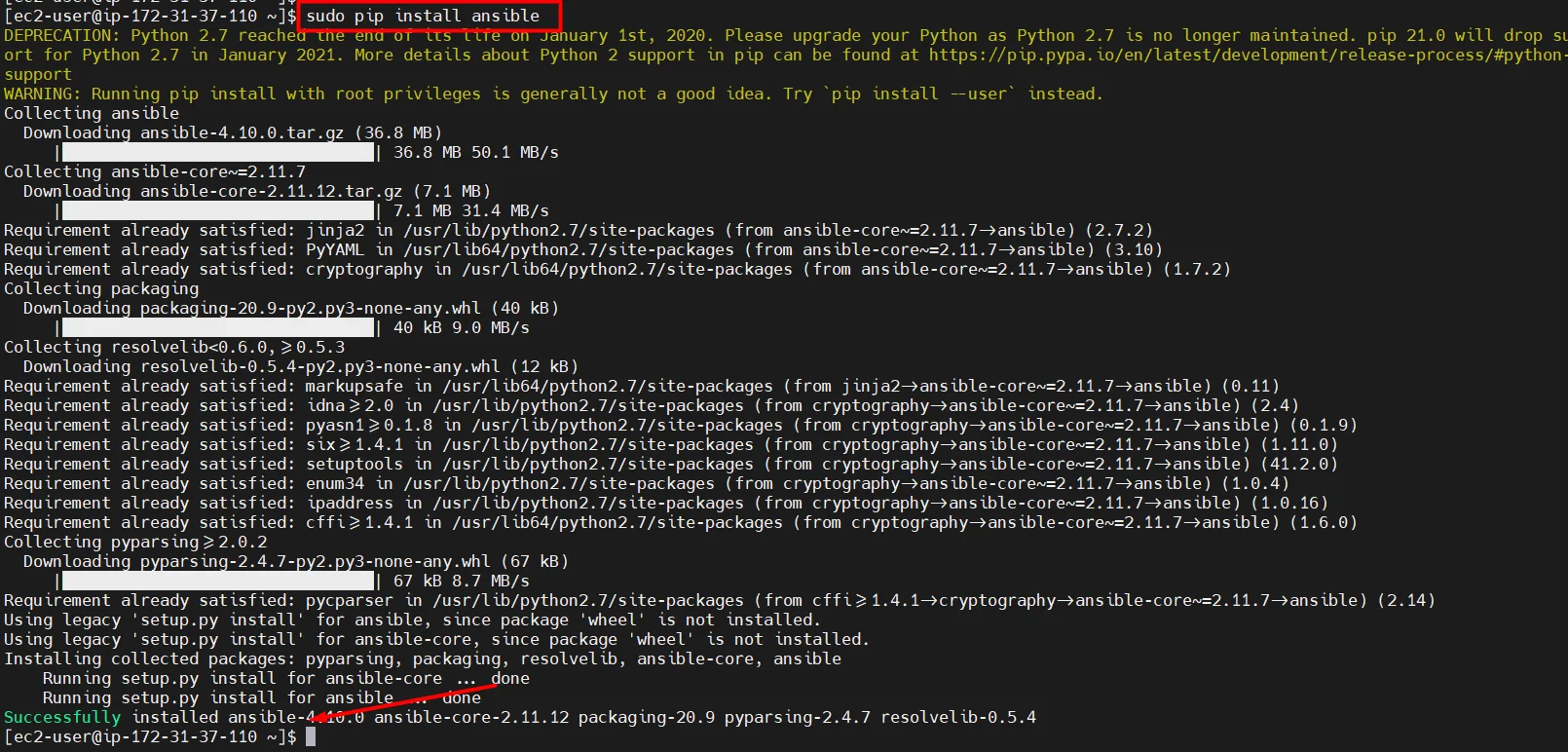
- Install Ansible
sudo pip install ansible
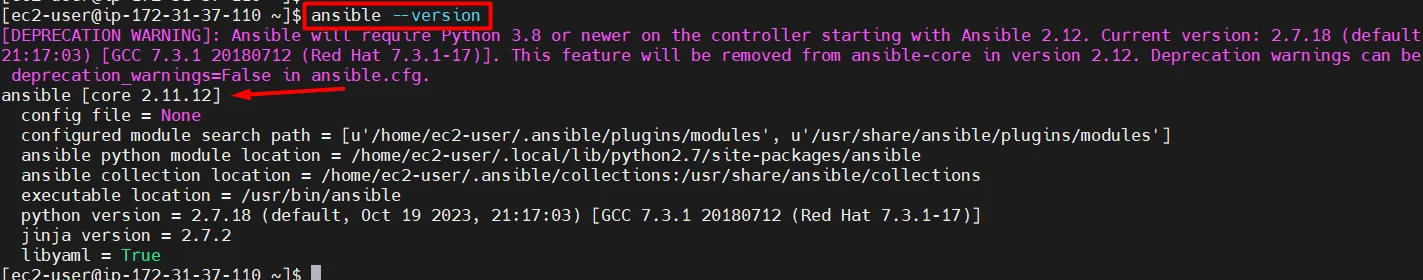
- Verify the Ansible installation by checking Ansible version
ansible --version
Install git and clone ansible script.
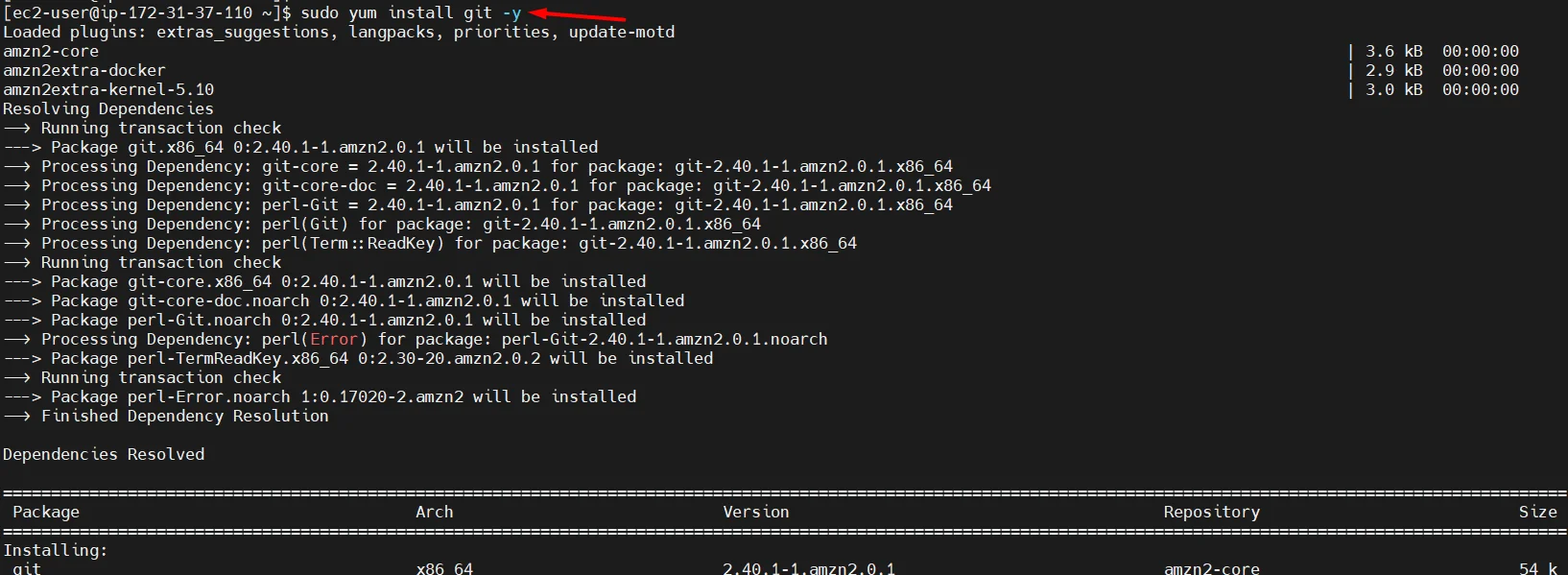
- install git
sudo yum install git -y
- clone the git repo which contains ansible script.
sudo git clone https://github.com/easydeploy-cloud/springboot_ansible.git
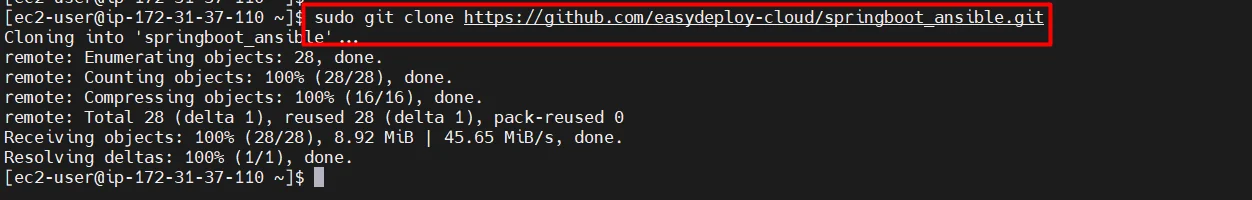
- Use the list command to verify whether we got the script or not
ls ls springboot_ansible
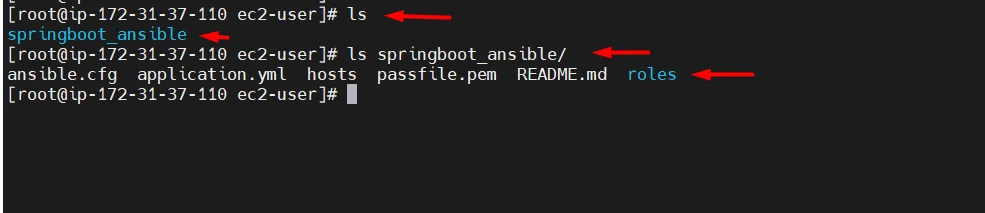
Here you will see a list of 5 files and 1 directory
- ansible.cfg = it contains the ansible configurations, we just need this file to run ansible.
- application.yml = it contains the host information and order of roles, like which role needs to execute first.
- hosts = it contains a list of hosts as a group.
- passfile.pem = it will contain your remote virtual machine’s private key.
- README.md = it contains some execution commands for your reference.
- roles = it contains the list of roles.
Alter the script to make it run.
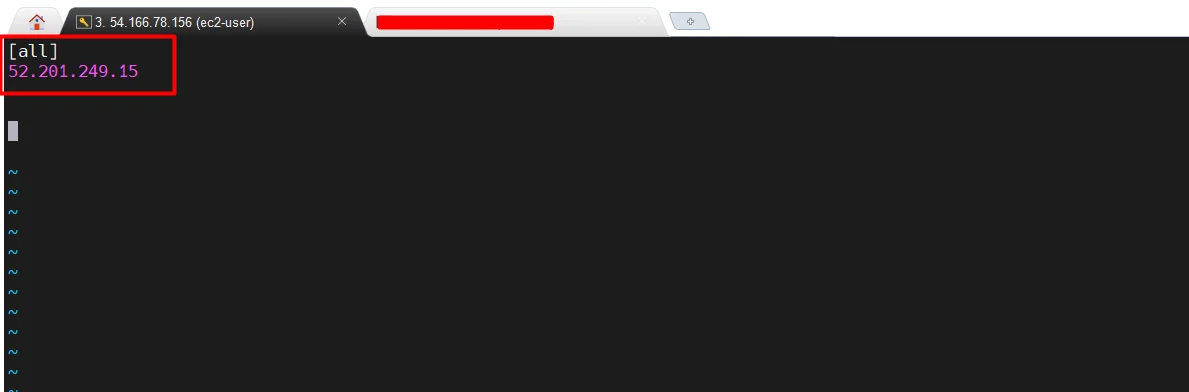
- Open the “hosts” file and add your remote server’s public ip address under the group “[all]” .
cd springboot_ansible ls sudo vi hosts
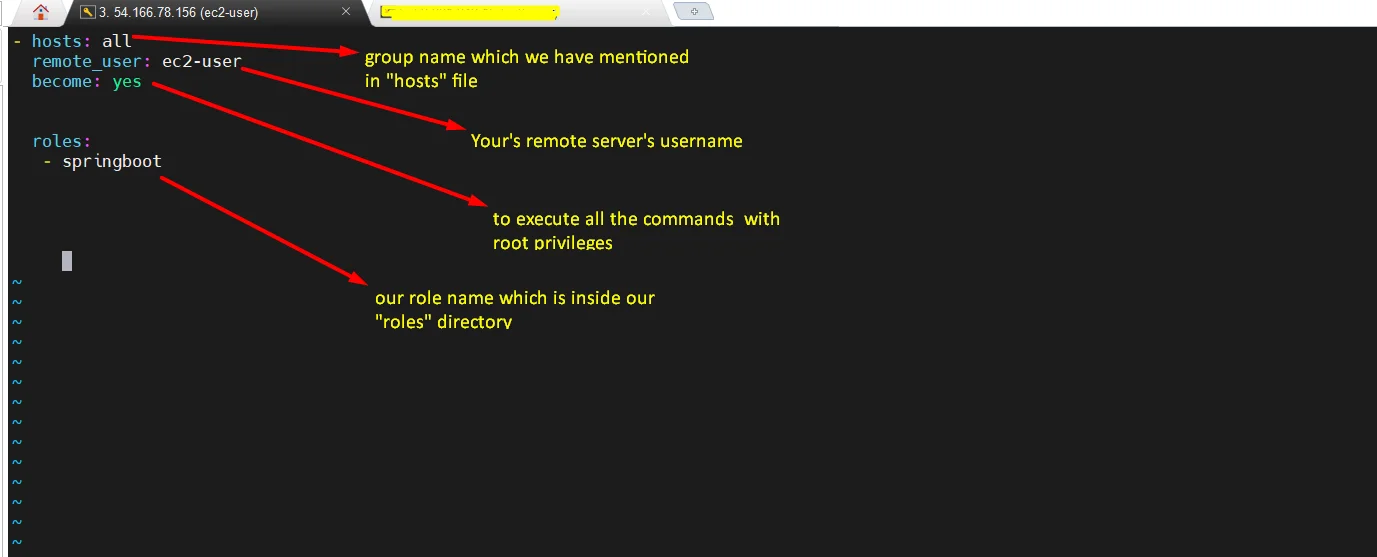
- Open the “application.yml” file and make sure your remote server’s username and host group, roles are correct.
sudo vi application.yml
- Open “passfile.pem” add your remote server’s private key and save.
sudo vi passfile.pem

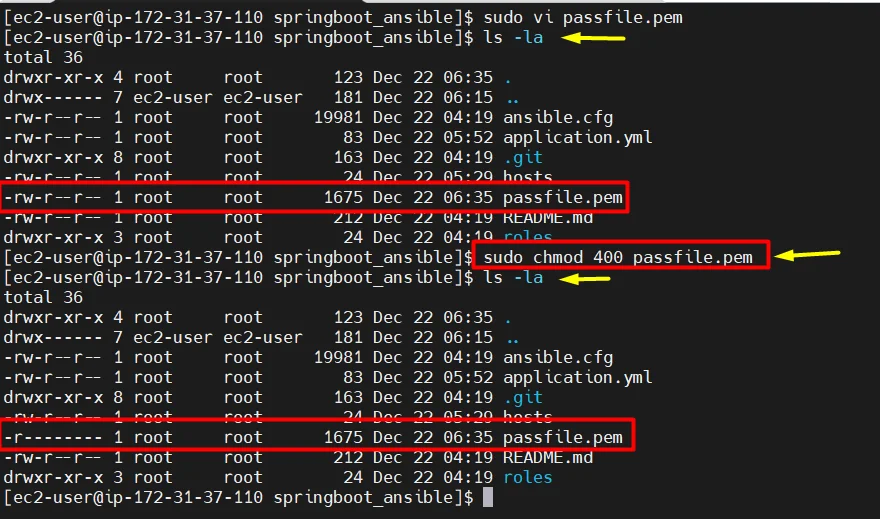
- Change the permission for “passfile.pem” file
ls -la sudo chmod 400 passfile.pem ls -la
Run the Ansible playbook command.
- This script will install Apache, java, and Maven, and also it will create separate Apache virtual host files with new users.
- You can view the command in this path ” cat roles/springboot/tasks/main.yml “
- Pass the required values to the variables
1. username = Username which you want to create in the remote server
2. domain name = Enter the domain name for your remote server, if you don’t have a domain use public IP instead.
ansible-playbook -i hosts -e "username=<username> domainname=<domainname> portno=8080" --private-key passfile.pem application.yml -vvv Eg: ansible-playbook -i hosts -e "username=basker domainname=techno.com portno=8080" --private-key passfile.pem application.yml -vvv
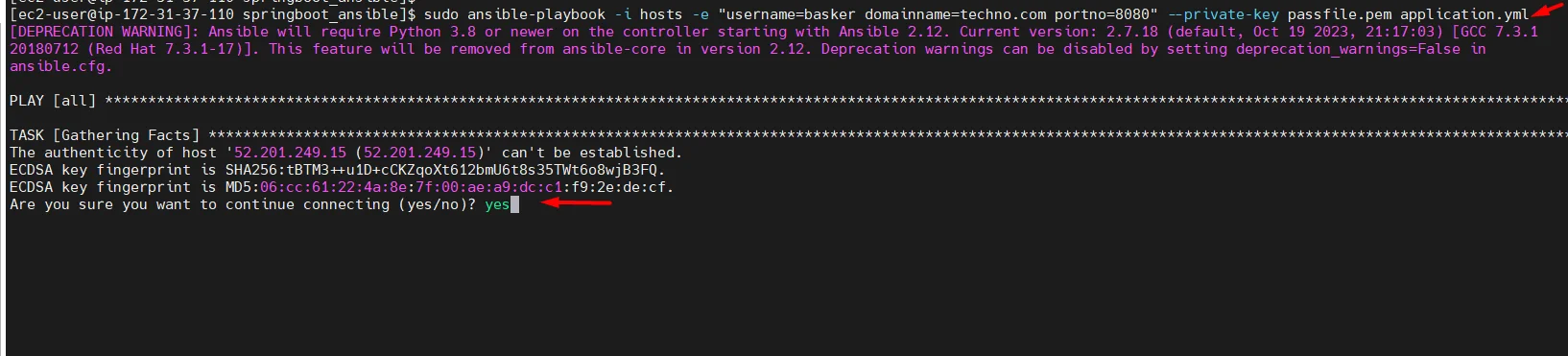
- Run the above command and wait until the script get completed.
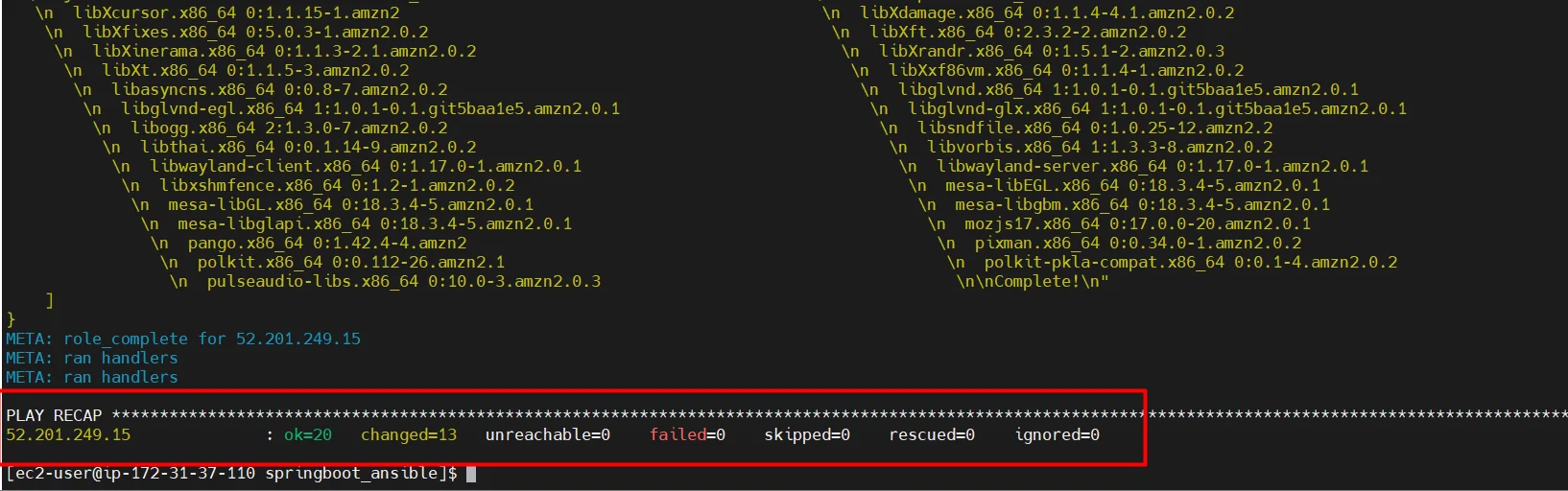
Now we have successfully installed all the dependencies to run “spring boot” applications lets verify the dependencies on the remote server one by one.
- Check whether the user is created or not
cd /home ls
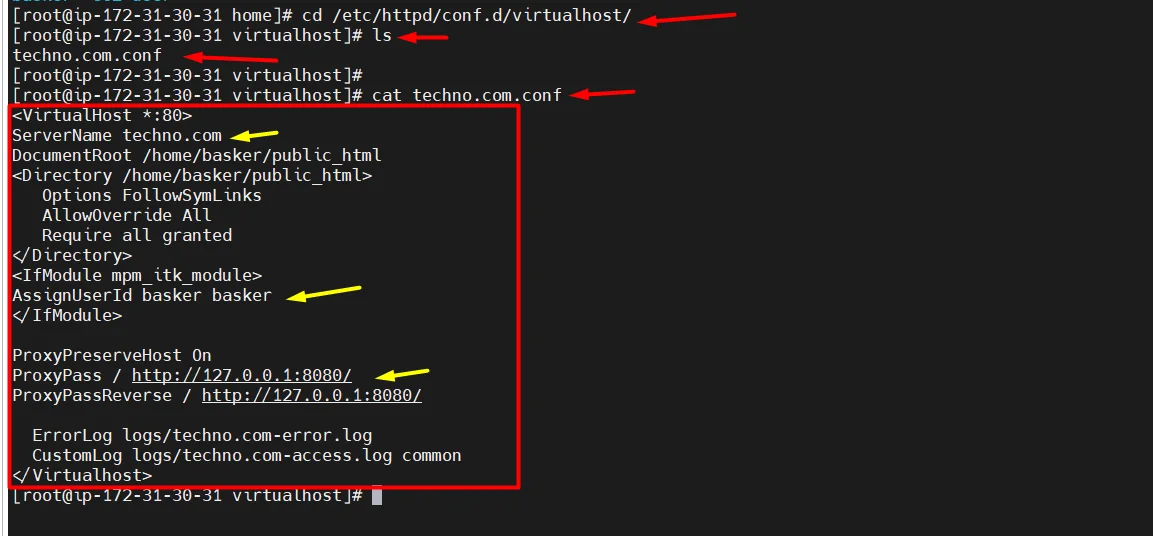
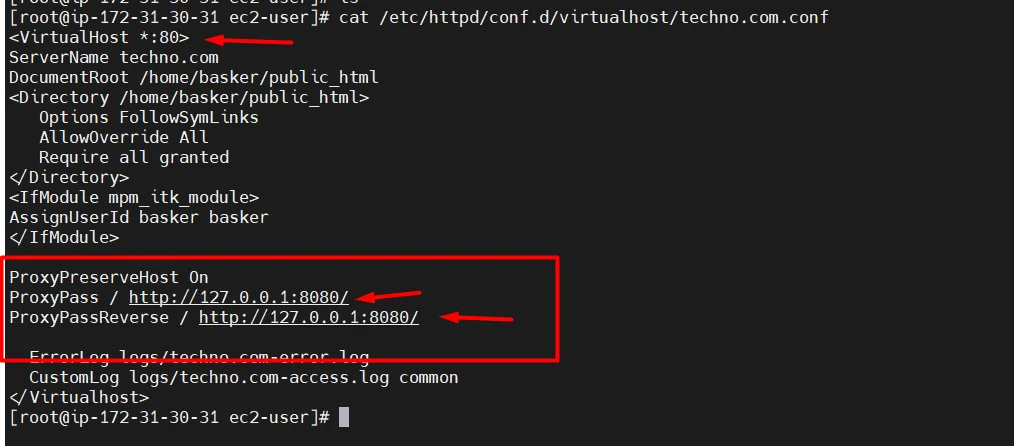
- There will be an Apache virtual host file with a new user.
cd /etc/httpd/conf.d/virtualhost/ ls cat techno.com.conf
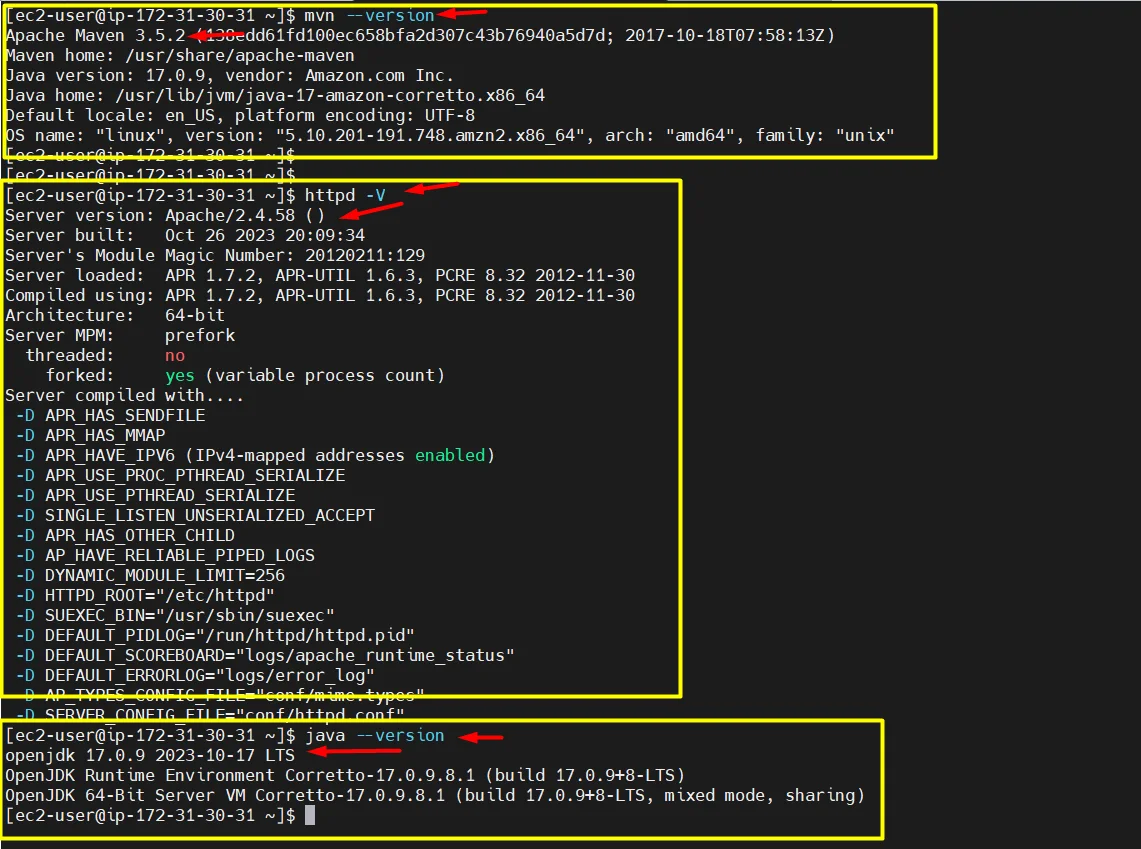
- check the version of Maven, apache, java
mvn --version httpd -V java --version
Run sample spring boot application
- goto your application working directory, which is “/home/<username>/public_html“
- clone sample spring boot application source code from git.
sudo su cd /home/basker/public_html pwd sudo git clone https://github.com/spring-guides/gs-spring-boot.git ls cd gs-spring-boot/initial/
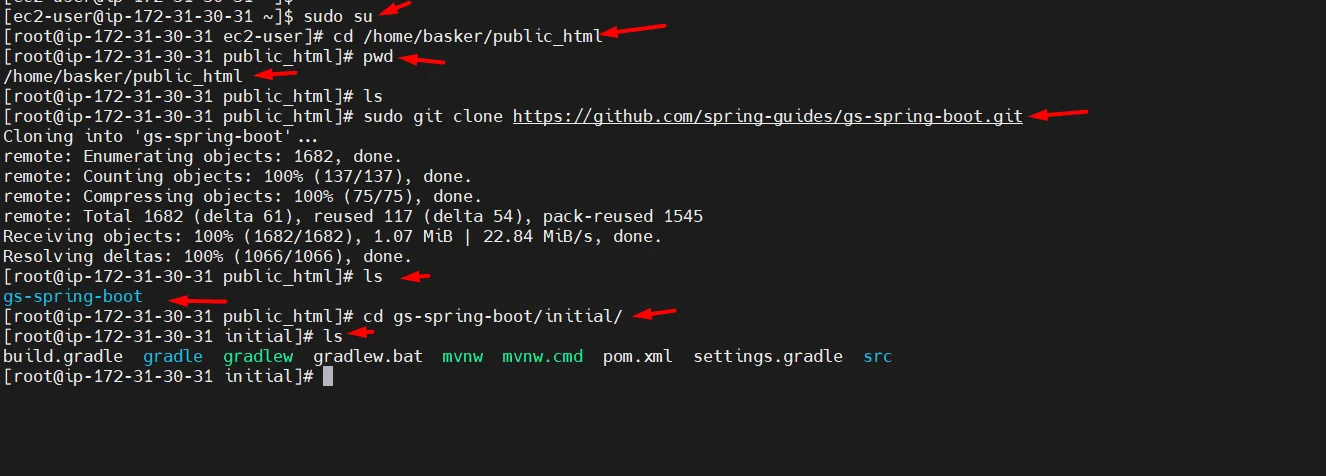
- Run your application using the below command
sudo mvn spring-boot:run
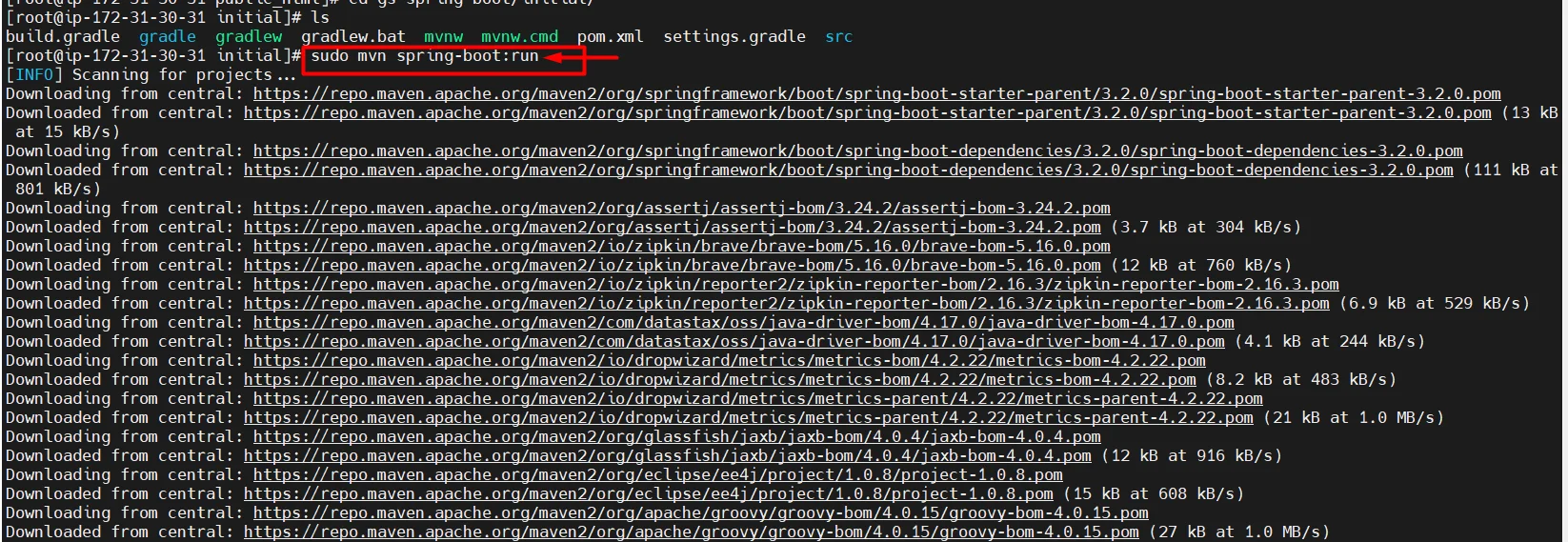
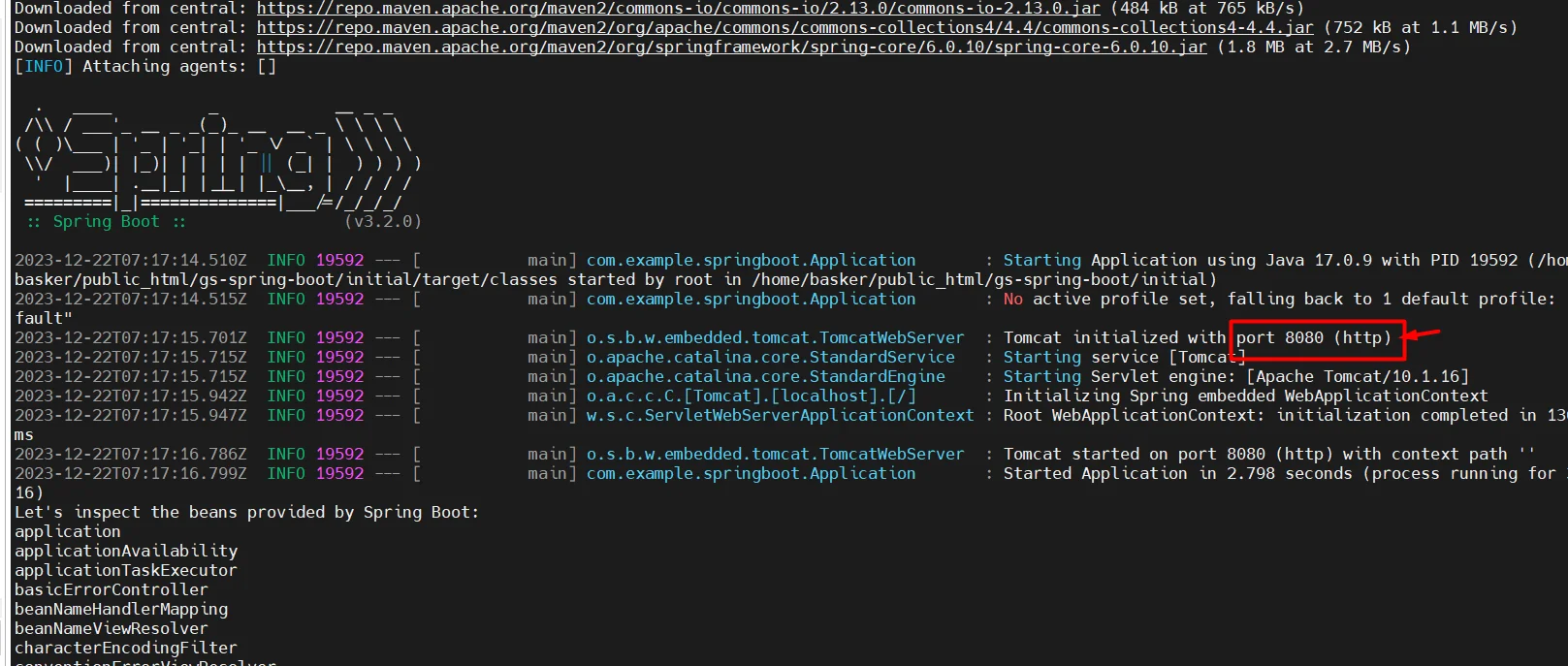
- Now copy your remote server’s public IP and check on a browser with ports 8080 and 80.
http://<publicip>:8080
http://<publicip>:80
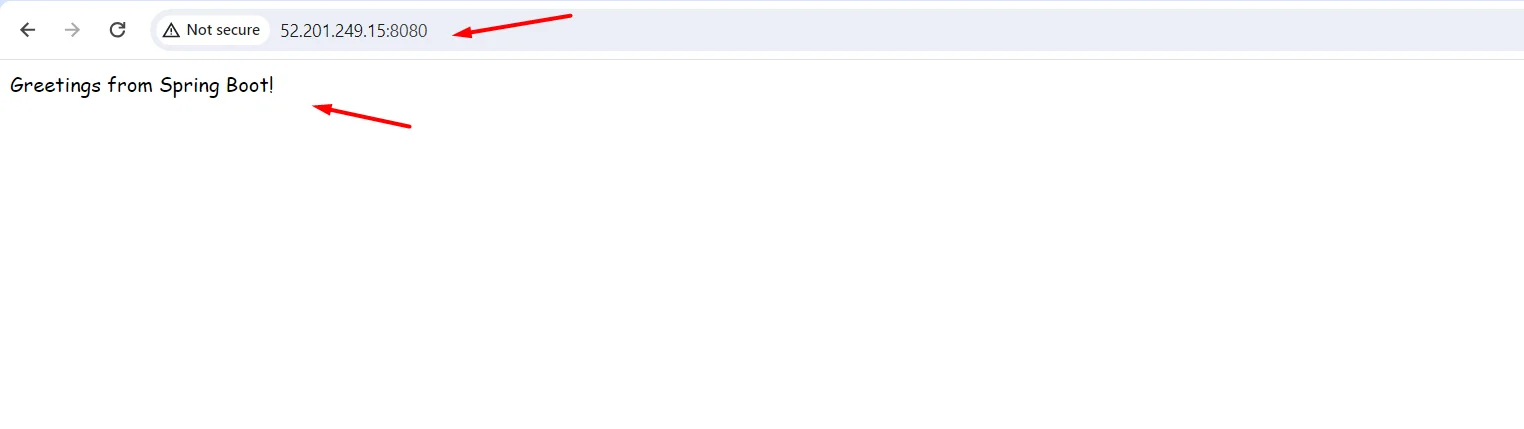
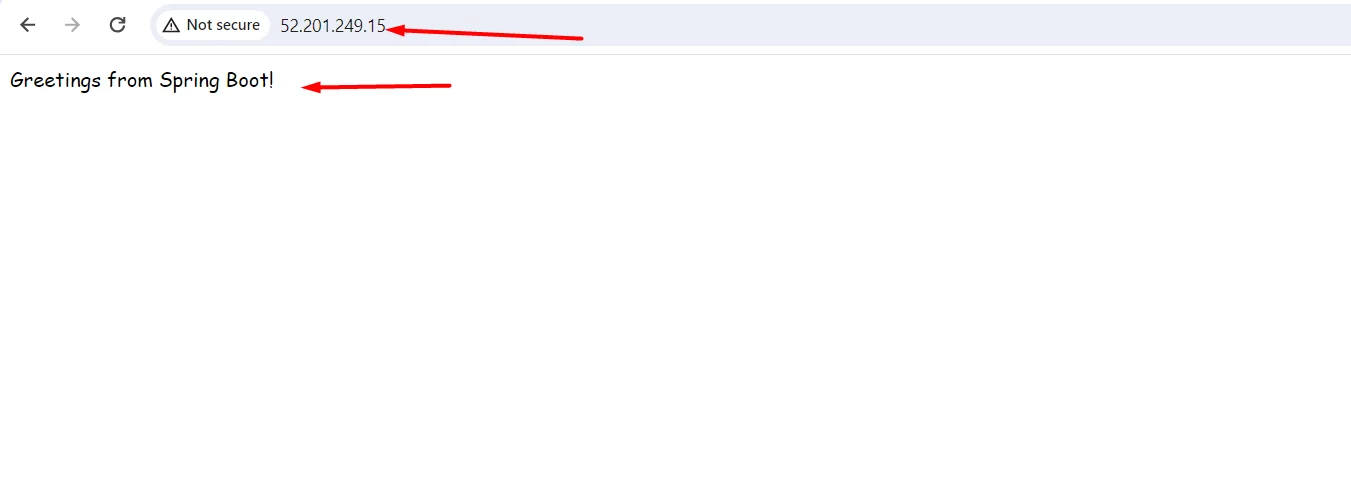
- Port “8080, 80” must be open in the server’s security group.
- our application will run in both 8080 and 80 because we have enabled a proxy between 8080 and 80 in the “apache virtual host file” so that, whatever traffic comes to 8080 will also come to 80.
Here the proxy configurations
You can also view the access log on the server.
Now we have Successfully completed our spring boot application setup with Ansible.!!